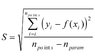- #1
TheDestroyer
- 402
- 1
Hi,
When I'm doing an experiment,
If the result of the experiment was some points, which I interpolate to create the linear function:
y=(a/b^2) x+c
while y is a function of x: y=f(x)
If the standard error in y was (S), How can I calculate the error in b?
Thank you
When I'm doing an experiment,
If the result of the experiment was some points, which I interpolate to create the linear function:
y=(a/b^2) x+c
while y is a function of x: y=f(x)
If the standard error in y was (S), How can I calculate the error in b?
Thank you