- #1
nekrofred
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
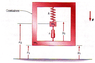
A mass-spring-damper subsystem is falling inside a container m1. The system is confined to the vertical direction. Use Lagrange’s equations to find the EOM.
A. Use x1 and x2 as generalized coordinates.
B. The linear spring is unstretched when x2 – x1 = l.
Homework Equations
See attached picture
The Attempt at a Solution
I know the block has to be restricted to only falling along the y-axis, and not moving in the x (2-D Problem). I need to set my constraints for that. Since it is a 1 DOF Problem, and there are 2 Bodies, There should only be 1 constraint needed. But where to put it. Also, how to determine the equations with the M-S-D system.