- #1
ThatGai
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
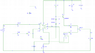
I am designing a circuit and trying to calculate the peak to peak voltage across the 8 ohm resistor. I'm getting 14 volts peak to peak output from the op amp. Any tips where I should start would be helpful.
I've attached my circuit to the post, Thanks
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
Since this is a design problem I am allowed to use software to play around with the circuit and measure the output, but I was wondering how would I calculate the voltage by hand.