- #1
dalarev
- 99
- 0
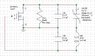
Attached is an image of the clapp oscillator I am designing, DC bias not shown.
My question is, how can I distinguish between the part of the circuit acting as the negative resistance generator and that which functions as a tank circuit?
The resistor shown in the image is not part of the DC bias.
My question is, how can I distinguish between the part of the circuit acting as the negative resistance generator and that which functions as a tank circuit?
The resistor shown in the image is not part of the DC bias.