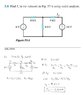
- #1
vg19
- 67
- 0
Hi,
I just have a quick question about nodal analysis in the attached file. At v1 and v3, is it not necessary to take into account the current going to the right and left respectivley?
So at v1, -6V + (v1 - v2 / 6k)
and at v3, 24V + (v2 - v3/4k)
Thanks a lot!
I just have a quick question about nodal analysis in the attached file. At v1 and v3, is it not necessary to take into account the current going to the right and left respectivley?
So at v1, -6V + (v1 - v2 / 6k)
and at v3, 24V + (v2 - v3/4k)
Thanks a lot!