- #1
Like Tony Stark
- 179
- 6
- Homework Statement
- Suppose two cases:
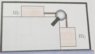
1) The room shown in the picture is static, and so are the blocks in it.
2) The room is being accelerated to the right, and the blocks are static with respect to each other
- Relevant Equations
- Newton's equations
I want you to tell me if I'm right
For 1), does ##m_2## feel a normal force? Because I don't think so, since it isn't pushing the wall.
For 2), ##m_2## suffers a normal force because it feels a pseudo-force to the left and so it pushes the wall
For 1), does ##m_2## feel a normal force? Because I don't think so, since it isn't pushing the wall.
For 2), ##m_2## suffers a normal force because it feels a pseudo-force to the left and so it pushes the wall