- #1
Drao92
- 72
- 0
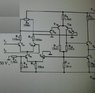
Hello everyone. I am studying internal structure of op amp and i don't know to solve some problems.
The problem is that i have to specify and justify which inputs of the differential stage are inverting and non-inverting input and i don't know how to do it. I tried to find the answer on google and on many many books but i didnt find anything to give me a clearly answer. Only thing i found is that we use the maximum and minimum value of common mode voltage but i didnt understand how.
I`ll also post some circuits if anybody can help me.
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=66211&stc=1&d=1391287797
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=66212&stc=1&d=1391287797
The problem is that i have to specify and justify which inputs of the differential stage are inverting and non-inverting input and i don't know how to do it. I tried to find the answer on google and on many many books but i didnt find anything to give me a clearly answer. Only thing i found is that we use the maximum and minimum value of common mode voltage but i didnt understand how.
I`ll also post some circuits if anybody can help me.
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=66211&stc=1&d=1391287797
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=66212&stc=1&d=1391287797