- #1
Micke
- 1
- 0
1. Question
Start with a organometallic (Benzene)M(Co)3see picture below) and React it with R- to get A, Then react A with I2 to get B and react A with H+ to get C. What is A,B and C?
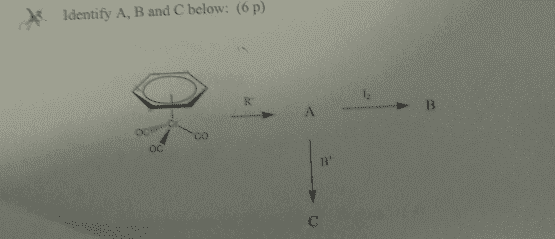
3. Attempt at answering the question.
I am not sure about the hapticity of Benzene. ? But i am prety sure that the first step is a Nucleophilic addition. Where R adds to the Metal, but i am not sure if one CO ligand will leave first or not.
I am more unsure about where the protonation will occur in C and I can not for my life figure out what B will be when A are reacted with I2. Sorry for the little information but i am desperate and do not know what else to write.
Start with a organometallic (Benzene)M(Co)3see picture below) and React it with R- to get A, Then react A with I2 to get B and react A with H+ to get C. What is A,B and C?
3. Attempt at answering the question.
I am not sure about the hapticity of Benzene. ? But i am prety sure that the first step is a Nucleophilic addition. Where R adds to the Metal, but i am not sure if one CO ligand will leave first or not.
I am more unsure about where the protonation will occur in C and I can not for my life figure out what B will be when A are reacted with I2. Sorry for the little information but i am desperate and do not know what else to write.
Last edited by a moderator: