- #1
nmsurobert
- 288
- 36
This is a review problem for an upcoming exam. I'm pretty sure a problem very similar to this will be on the exam. And surprise surprise I'm freaken lost.
1. Homework Statement
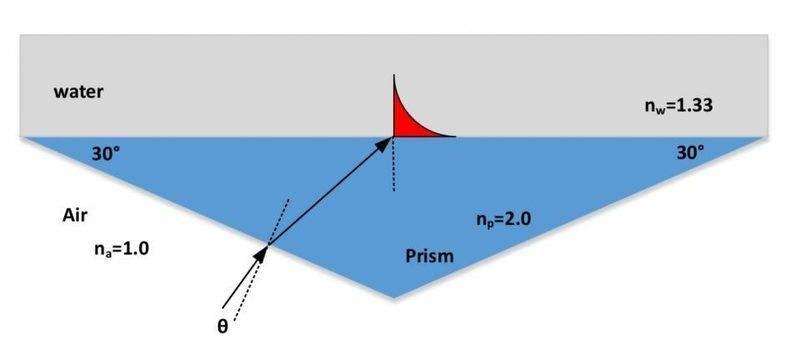
A high index prism is used to launch an evanescence wave at the water/prism interface as shown. A He-Ne laser (λ = 623 mm) is used as the light source.
a) find the required angle to excite the evanescence wave.
b) calculate the penetration depth, the distance into the water at which the amplitude of the evanescence wave has dropped to a value of 1/e of its maximum value at the interface, into the water.
This is the picture connected to the problem.
For part (a) I thought sinθ*n1 = sin90*n2, where n1 = 1 and n2 = 2, solve for θ would give me a solution. It did for for one of his homework assignments. But it doesn't work here.
For (b) I think I need to get the answer to part (a) first but even then I'm still stuck. My book had two sentences related to penetration depth so it's no help at all.
1. Homework Statement
A high index prism is used to launch an evanescence wave at the water/prism interface as shown. A He-Ne laser (λ = 623 mm) is used as the light source.
a) find the required angle to excite the evanescence wave.
b) calculate the penetration depth, the distance into the water at which the amplitude of the evanescence wave has dropped to a value of 1/e of its maximum value at the interface, into the water.
This is the picture connected to the problem.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
For part (a) I thought sinθ*n1 = sin90*n2, where n1 = 1 and n2 = 2, solve for θ would give me a solution. It did for for one of his homework assignments. But it doesn't work here.
For (b) I think I need to get the answer to part (a) first but even then I'm still stuck. My book had two sentences related to penetration depth so it's no help at all.