- #1
mtrl
- 6
- 0
I am studying on the electrical properties of organic compounds and having a problem with photoinduced absorption spectroscopy applied to these materials. Because in all the books, articles, etc , information given is on the results of applying this method. However i need to learn what PIA exactly is, what happens in terms of charge carriers when an organic compound is excited during PIA...
For example, the following picture is from an article that I am reading.
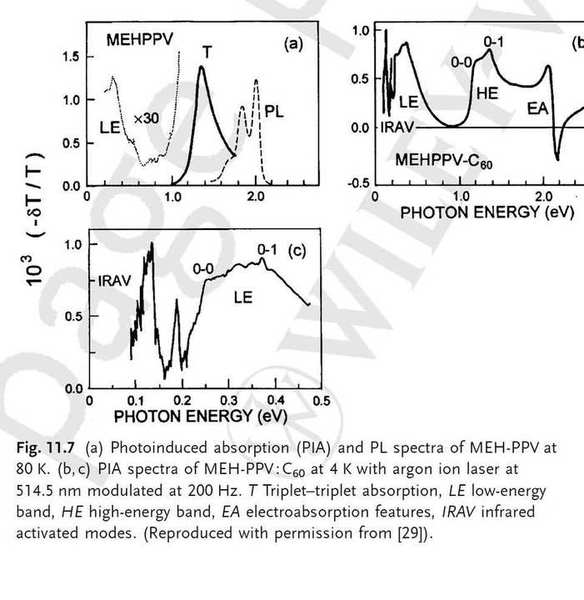
I do not even know what the variable on the vertical axis stands for.
Can someone please advice me a source which supplies information on the theory of PIA and similar studies applied to organics?
For example, the following picture is from an article that I am reading.
I do not even know what the variable on the vertical axis stands for.
Can someone please advice me a source which supplies information on the theory of PIA and similar studies applied to organics?