- #1
casiocasio442
- 1
- 0
Thread moved from the technical forums, so no Homework Template is shown.
Summary:: I cannot seem to get the answer to the following question.
For (a) I am using the formula 1/V= 1/U- 1/F, giving me 7.5cm. I am then adding this to 50cm to get 57.5cm. I then used -1/20-1/57.5-1/v to get **-14.9cm** which is Incorrect.
Any help greatly appreciated!
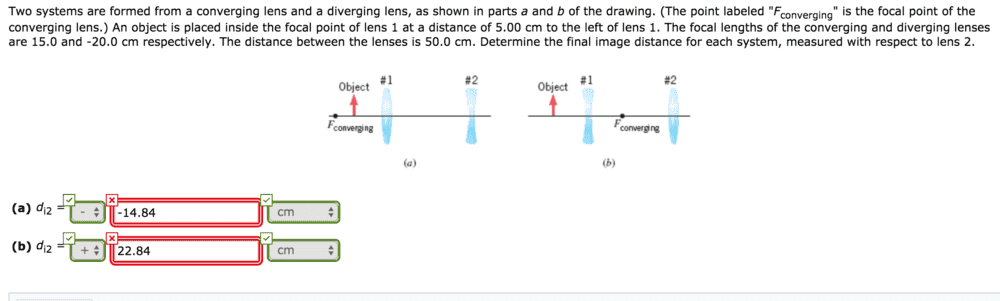
For (a) I am using the formula 1/V= 1/U- 1/F, giving me 7.5cm. I am then adding this to 50cm to get 57.5cm. I then used -1/20-1/57.5-1/v to get **-14.9cm** which is Incorrect.
Any help greatly appreciated!