- #1
luigihs
- 86
- 0
With Vout not connected to any additional circuitry, what power is dissipated in the 7 k resistor?
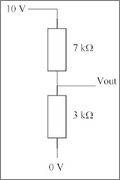 So I am trying to get the power in 7k resistor I know the formula if I need to get Vout but in the question it says that the vout is not connected to any additional circuitry so I assume that I don't have to use the Vout so is Vin / resistor in this case 10 / 7 = 1.42 <-- but this is the resistance how I am suppose to get the power?
So I am trying to get the power in 7k resistor I know the formula if I need to get Vout but in the question it says that the vout is not connected to any additional circuitry so I assume that I don't have to use the Vout so is Vin / resistor in this case 10 / 7 = 1.42 <-- but this is the resistance how I am suppose to get the power?
Im assuming this from the potential divider I = Vin / R1 + R2 . Now Ohms laws say that V = I x R so if I get the total resistance between 7 + 3 = 10 divided by the voltage 10 / 10 = 1 but I still stuck because I am getting the total voltage I want only the power in 7k I am confused help me thanks!
Im assuming this from the potential divider I = Vin / R1 + R2 . Now Ohms laws say that V = I x R so if I get the total resistance between 7 + 3 = 10 divided by the voltage 10 / 10 = 1 but I still stuck because I am getting the total voltage I want only the power in 7k I am confused help me thanks!