- #1
Lone Wolf
- 10
- 1
- Homework Statement
- A particle of mass M = 1 kg is subject to a force F with associated potential energy U(x, y) = x^2 + y^2 (x and y in m).
a) Find F(x, y)
b) Find the equilibrium position
c) Suppose the particle has a circular trajectory around the origin. Find the radius when the total energy is 2 J.
- Relevant Equations
- F = - grad U
a)
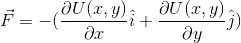
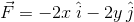
Solution given: F = - x î - y j
b)
The equilibrium position happens when F = 0.
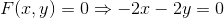
x = 0 and y = 0 is the point of equilibrium.
Solution given: (0, 0)
c)
Since the particle has a circular trajectory the trajectory equation becomes x^2 + y^2 = R^2.
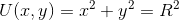
The maximum potential energy the system can achieve is 2 J (= total energy).
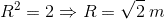
Solution given: R = 1 m
Any help is appreciated.
Solution given: F = - x î - y j
b)
The equilibrium position happens when F = 0.
x = 0 and y = 0 is the point of equilibrium.
Solution given: (0, 0)
c)
Since the particle has a circular trajectory the trajectory equation becomes x^2 + y^2 = R^2.
The maximum potential energy the system can achieve is 2 J (= total energy).
Solution given: R = 1 m
Any help is appreciated.