- #1
sayf alawneh
- 8
- 0
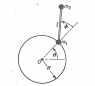
the question is : particles m1 and m2 each of mass m are connected by a massless rod with length l , these particles move on a frictionless horizontal plane as shown in the screen shot , the movement of m1 is fixed on a frictionless circular track of radius R , find the E.O.M !
here we can find T and V and use the lagrangian easily
i found the kinetic energy and found the potential energy but for some reason my doctor said that the potential energy is zero for this system can anybody tell me why , please i need help :(
also i solved for theta and phy but the doctor said that this system can be solved for theta only considering it the only degree of freedom ! why is that we have 2 degrees of freedom theta and phy so why we consider theta the only degree of freedom ![/B]
Homework Equations
here we can find T and V and use the lagrangian easily
The Attempt at a Solution
i found the kinetic energy and found the potential energy but for some reason my doctor said that the potential energy is zero for this system can anybody tell me why , please i need help :(
also i solved for theta and phy but the doctor said that this system can be solved for theta only considering it the only degree of freedom ! why is that we have 2 degrees of freedom theta and phy so why we consider theta the only degree of freedom ![/B]