- #1
Jack_O
- 65
- 0
Problem:
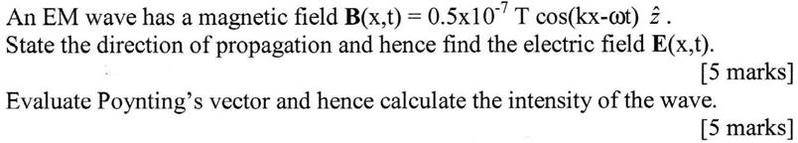
Attempt:

I think I've done the first bit correctly (but I'm not certain). As for the second half of the question I'm at a loss. I have looked up poyntings vector and found S=ExH where H is the auxiliary magnetic field (i'm not sure what this means) and S=(1/u(0)) (ExB), but I'm not sure what to do with it.
Any help appreciated.
Attempt:
I think I've done the first bit correctly (but I'm not certain). As for the second half of the question I'm at a loss. I have looked up poyntings vector and found S=ExH where H is the auxiliary magnetic field (i'm not sure what this means) and S=(1/u(0)) (ExB), but I'm not sure what to do with it.
Any help appreciated.