- #1
Baquedano
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
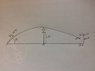
A soccer ball is kicked 27.43m away from the goal and 9.15m away from the defensive line with a initial velocity of 36 m/s, when the ball reaches the goal is 1.92m from the floor [/B]
I'll leave a little diagram of the problem, thanks for your time.
P.D: I apologize for my poor English, I hope you understood what I was trying to say