- #1
Rugile
- 79
- 1
Homework Statement
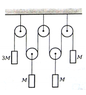
No friction, pulleys and also string are weightless, the tension through the string is distributed uniformly. Find the acceleration of the mass 3M (see image attached)
Homework Equations
II law of Newton
The Attempt at a Solution
Well I wrote such equations for all pulleys (counting pulleys from right to left):
1) M*a1 = T - Mg;
2) M*a2 = 2T - Mg;
4) M*a3 = 2T - Mg;
5) 3M*a = T - 3Mg.
Now we have 1 more unknowns than equations. Any ideas?