- #1
Saladsamurai
- 3,020
- 7
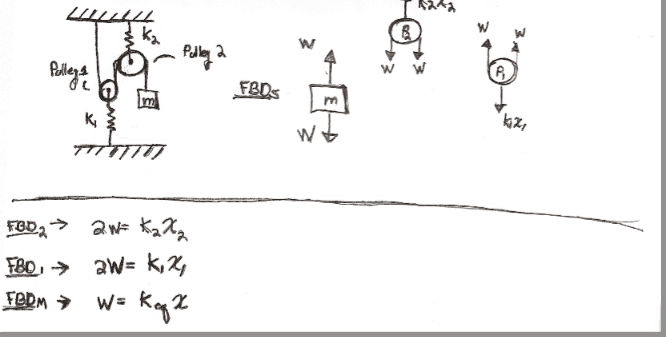
So I am trying to follow along this example in the text to find keq of the system.
I can follow everything up until the point that they say: "It follows that x=2(x1+x2)
where:
x = displacement of mass
x1 =displacement of Pulley1cm
x2 =displacement of Pulley2cm
I am not seeing it. I am also very tired. So please help me and then slap me
I can follow everything up until the point that they say: "It follows that x=2(x1+x2)
where:
x = displacement of mass
x1 =displacement of Pulley1cm
x2 =displacement of Pulley2cm
I am not seeing it. I am also very tired. So please help me and then slap me