- #1
adjacent
Gold Member
- 1,552
- 63
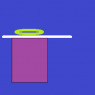
The Coin(Green) in lying on a paper which is lying on a box.When I pull the paper with a higher force so that I could remove it easily,the coins stays about the same place.
When I remove the paper slowly,the coin comes with the paper.
Why?
I think that objects can react(Move) to smaller forces easily but for larger forces,it doesn't.
What do you think?
When I remove the paper slowly,the coin comes with the paper.
Why?
I think that objects can react(Move) to smaller forces easily but for larger forces,it doesn't.
What do you think?
Attachments
Last edited: