- #1
MG5
- 60
- 0
In this picture...
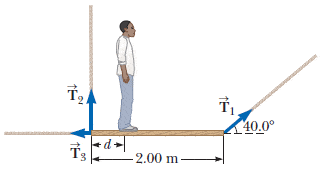
Why do T2 and T3 not produce any torque? Something to do with it being in equilibrium? Thanks.
Why do T2 and T3 not produce any torque? Something to do with it being in equilibrium? Thanks.
Torque is a measure of the force that causes an object to rotate around an axis. It is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance from the axis of rotation. The unit for torque is Newton-meters (N-m).
The two main types of torque are static torque and dynamic torque. Static torque is the force applied to an object that is not in motion, while dynamic torque is the force applied to an object that is in motion. Other types of torque include self-torque, which is the torque generated by a rotating object, and external torque, which is the torque applied to an object by an external force.
Torque plays a crucial role in rotational motion as it determines the rate at which an object rotates around an axis. The greater the torque applied, the faster the object will rotate. Additionally, torque also affects the stability of an object's rotational motion. A higher torque will make an object more stable and less prone to changes in its rotational motion.
The factors that affect torque include the magnitude, direction, and point of application of the force applied to an object. The distance between the axis of rotation and the point of application of the force also affects torque, with a longer distance resulting in a higher torque. Additionally, the mass and shape of an object can also affect its torque.
Torque has many practical applications, including in the design and operation of machines and vehicles. It is used in engines to generate the rotational motion needed to power vehicles. Torque is also important in construction and engineering, as it is used to tighten bolts and screws to the appropriate level. In sports, torque is used to enhance performance, such as in swinging a baseball bat or golf club.