- #1
mpn17
- 7
- 0
Homework Statement
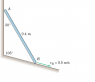
The ends of the slender bar remain in contact with their respective support surfaces. If end has a velocity in the direction shown, determine the angular velocity of the bar and the velocity of end.
Answers:
ω=1.394 rad/s VA=0.408 m/s down
Homework Equations
Va=Vb +Va/b
law of sines
V=rw
The Attempt at a Solution
I've tried using the angles given to use the law of sines and the velocity given into find Va/b or Va and then using V=rω to find the angular velocity but have had no luck. Any help would be appreciated
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: