- #1
bj5110
- 2
- 0
A 1.0 kg block is held in place against a spring with spring constant k = 100 N/m (see the figure, below) by a horizontal external force. The spring is compressed 20 cm. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with some (horizontal) velocity upon separation from the spring. The block descends a ramp with height h = 2.0 m. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction over this section is 0.30. The block slides through this rough section a distance S, and comes to a stop at point D.
What is the sliding distance S?
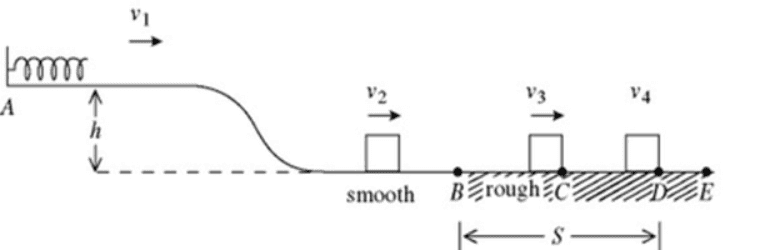
Can someone please tell me if my below attempt is the correct answer?
Find velocity after reaches bottom of hill (by conservation of mechanical energy)
( 1/2 * k * x2 ) + ( 1/2 * m * g ) = 1/2 * m * v2
(1/2 * 100 * .20) + (1/2 * 1 * 9.8) = 1/2 * 1 * v2
14.9 = 1/2 * v2
v ≈ 5.4589 m/s
Find the acceleration once it hits the rough spot
μmg = Fnet
0.30 * 1 * 9.8 = 2.94 N
2.94 N = m * a
2.94 N = 1 * a
a = -2.94 m/s2
Kinematics to find distance of S
vf2 = vi2 + 2ax
0 = 5.45892 + ( 2 * -2.94 * x)
x = 5.068 m
What is the sliding distance S?
Can someone please tell me if my below attempt is the correct answer?
Find velocity after reaches bottom of hill (by conservation of mechanical energy)
( 1/2 * k * x2 ) + ( 1/2 * m * g ) = 1/2 * m * v2
(1/2 * 100 * .20) + (1/2 * 1 * 9.8) = 1/2 * 1 * v2
14.9 = 1/2 * v2
v ≈ 5.4589 m/s
Find the acceleration once it hits the rough spot
μmg = Fnet
0.30 * 1 * 9.8 = 2.94 N
2.94 N = m * a
2.94 N = 1 * a
a = -2.94 m/s2
Kinematics to find distance of S
vf2 = vi2 + 2ax
0 = 5.45892 + ( 2 * -2.94 * x)
x = 5.068 m