- #1
Ylle
- 79
- 0
Hello...
I have a little problem I hope you guys can help me with.
I'll write down the problem-text first, so it will be easier to point out the problem - hopefully.
Here it goes:
Event E0 has the following coordinates in some frame S:
x = 2 m
ct = 4 m
Locate E0 on a space-time diagram for frame S. Draw the lines that define the three invariant regions of space-time for E0. On the diagram, locate each of the follow events:
E1: x = 0, ct = 1 m
E2: x= 4 m, ct = 2 m
E3: x = 4 m, ct = 5 m
Specify whether each event is on the light cone of E0, in the past or the future of E0, or in the elsewhere. If E is within one of the light cones, find the speed (relative to S) of a frame in which E occurs at the same place as E0. If E is in the elsewhere of E0, find the speed if a frame in which it is simultaneous with E0.
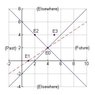
First I draw my diagram, as you can see on the image, define the invariant regions (Past, future and 2x elsewhere), and locate the 3 events.
The next question is to specify where the events are happening.
I get:
E1 = The past
E2 = On the light cone
E3 = In the elsewhere
The next question is to find the speed (relative to S) of a frame in which E occurs at the same place as E0.
Then I draw the red line, and get the speed: (2/3)c
And that's what I got so far. The last part "If E is in the elsewhere of E0, find the speed if a frame in which it is simultaneous with E0." I cannot understand.
So maybe you can help me out ?
Thank you
- Ylle
I have a little problem I hope you guys can help me with.
I'll write down the problem-text first, so it will be easier to point out the problem - hopefully.
Here it goes:
Event E0 has the following coordinates in some frame S:
x = 2 m
ct = 4 m
Locate E0 on a space-time diagram for frame S. Draw the lines that define the three invariant regions of space-time for E0. On the diagram, locate each of the follow events:
E1: x = 0, ct = 1 m
E2: x= 4 m, ct = 2 m
E3: x = 4 m, ct = 5 m
Specify whether each event is on the light cone of E0, in the past or the future of E0, or in the elsewhere. If E is within one of the light cones, find the speed (relative to S) of a frame in which E occurs at the same place as E0. If E is in the elsewhere of E0, find the speed if a frame in which it is simultaneous with E0.
First I draw my diagram, as you can see on the image, define the invariant regions (Past, future and 2x elsewhere), and locate the 3 events.
The next question is to specify where the events are happening.
I get:
E1 = The past
E2 = On the light cone
E3 = In the elsewhere
The next question is to find the speed (relative to S) of a frame in which E occurs at the same place as E0.
Then I draw the red line, and get the speed: (2/3)c
And that's what I got so far. The last part "If E is in the elsewhere of E0, find the speed if a frame in which it is simultaneous with E0." I cannot understand.
So maybe you can help me out ?
Thank you
- Ylle
Attachments
Last edited: