- #1
unreal89
- 8
- 0
Homework Statement
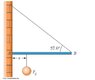
One end of a uniform 4.00-m-long rod of weight Fg is supported by a cable. The other end rests against the wall, where it is held by friction, as in Figure below. The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is s = 0.500. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional weight Fg (the same as the weight of the rod) can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A.
Homework Equations
TORQUEnet = (F)1(d)1 + (F)2(d)2 + ...
The Attempt at a Solution
Assuming fulcrum is at the right tip of the bar
TORQUEnet = 2Fg + 4Ff - x Fg