- #1
koolkuzz
- 5
- 0
Thermodynamics problem...
I am stuck on the following problem:
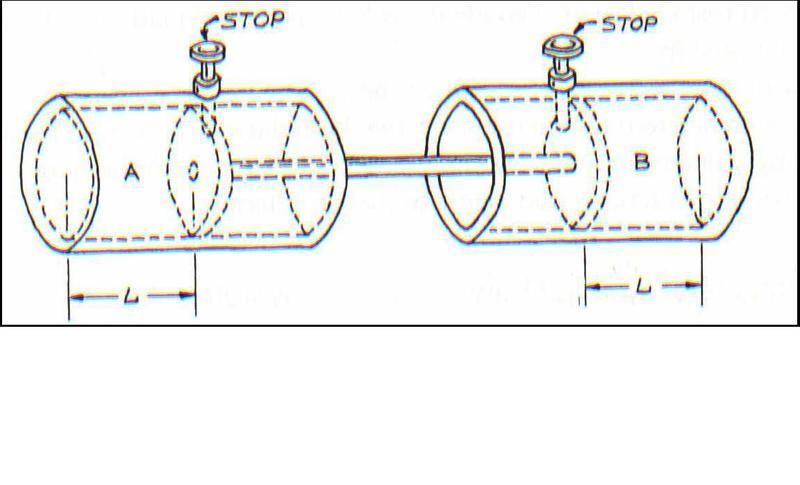
"Two well-insulated cylinders are placed as shown in Figure . The pistons in both cylinders are of identical construction.
The clearances between piston and wall are also made identical in both cylinders. The pistons and the connecting rod are
metallic.
Cylinder A is filled with gaseous helium at 2 bar and cylinder B is filled with gaseous helium at 1 bar. The temperature
is 300 K and the length L is 10 cm. Both pistons are only slightly lubricated.
The stops are removed. After all oscillations have ceased and the system is at rest, the pressures in both cylinders are,
identical.
1. Assuming that the gases are ideal with a constant Cv and assuming that the masses of the cylinder and pistons are
negligible (any energy changes of pistons and cylinders can be neglected), what are the final temperatures?
2. Consider the situation with well-insulated pistons and connecting rods of low thermal conductivity. What are the
final temperatures after the oscillations have ceased and the pressures have equalized?"
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
I am stuck on the following problem:
"Two well-insulated cylinders are placed as shown in Figure . The pistons in both cylinders are of identical construction.
The clearances between piston and wall are also made identical in both cylinders. The pistons and the connecting rod are
metallic.
Cylinder A is filled with gaseous helium at 2 bar and cylinder B is filled with gaseous helium at 1 bar. The temperature
is 300 K and the length L is 10 cm. Both pistons are only slightly lubricated.
The stops are removed. After all oscillations have ceased and the system is at rest, the pressures in both cylinders are,
identical.
1. Assuming that the gases are ideal with a constant Cv and assuming that the masses of the cylinder and pistons are
negligible (any energy changes of pistons and cylinders can be neglected), what are the final temperatures?
2. Consider the situation with well-insulated pistons and connecting rods of low thermal conductivity. What are the
final temperatures after the oscillations have ceased and the pressures have equalized?"
Any help would be greatly appreciated.