- #1
Pi-Bond
- 302
- 0
Homework Statement
(Kleppner & Kolenkow- An Introduction to Mechanics - 2.15)
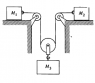
The image shows the setup. The task is to find the tension in the rope. The coefficient of friction of the sliding blocks with the surface is [itex]\mu[/itex], and the string is of constant length.
Homework Equations
Newton's Laws
The Attempt at a Solution
The question is easy enough if the accelerations of the three blocks can be related. I argued that when the lower block moves down a distance x3, the pulley above it draws a string length equal to x3. Since the length is constant, the string length drawn must equal the distance moved by the sliding blocks, i.e.
x3=x1+x2
Differentiating twice with respect to time yields:
a3=a1+a2
However this relationship yields the wrong answer. Any pointers on the correct relationship?