- #1
HoneyPi
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
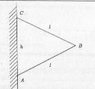
A uniform beam AB, of lenth l and mass m, is free in turn in a vertical plane about a smooth hinge at A. It is supported in a static position by a light string, of the same length l, attached to the end of end B of the beam and to an anchoring point C at a height h vertically above A.
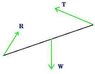
- Draw a diagram showing clearly all the external forces acting on the beam.
- By considering the equilibrium conditions for the beam, find an expression for the tension in the string in terms of m, l, h and g, the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity.
Homework Equations
[tex]
\textbf{R} = R_j \textbf{j} + R_k \textbf{k}
[/tex]
[tex]
\textbf{W} = -mg \textbf{k}
[/tex]
[tex]
\textbf{T} = - \textsl{T} \cos\theta \textbf{j} + \textsl{T} \sin\theta \textbf{k}
[/tex]
[tex]
\textbf{r}_R = \textbf{0}
[/tex]
[tex]
\textbf{r}_W = \frac{1}{2} l \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \textbf{j}
[/tex]
[tex]
\textbf{r}_T = l \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \textbf{j}
[/tex]
The Attempt at a Solution
(i)
(ii) Determining the torques:
[tex]
\boldsymbol{\Gamma}_R = \textbf{0}
[/tex]
[tex]
\boldsymbol{\Gamma}_W = \frac{1}{2} l \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \textbf{j} \times -mg \textbf{k} = - \frac{1}{2} l m g \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \textbf{i}
[/tex]
[tex]
\boldsymbol{\Gamma}_T = l \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \textbf{j} \times \textsl{T} \sin\theta \textbf{k} = l \textsl{T} \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \sin\theta \textbf{i}
[/tex]
Then since we consider the equilibrium conditions, we have
[tex]
\boldsymbol{\Gamma}_T + \boldsymbol{\Gamma}_W + \boldsymbol{\Gamma}_R = \textbf{0}
[/tex]
Solving this in i-direction gives:
[tex]
l \textsl{T} \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta) \sin\theta = \frac{1}{2} l m g \cos(\frac{1}{2} \theta)
\Rightarrow \textsl{T} \sin\theta = \frac{1}{2} m g
[/tex]
And now I am not sure about the following:
Since
[tex] \sin(\frac{1}{2} \theta) = \frac{\frac{1}{2} h }{l}[/tex]
it follows that
[tex] 2 \sin(\frac{1}{2} \theta) = \sin\theta = \frac{h}{l}[/tex]
And so
[tex]
\textsl{T} \frac{h}{l} = \frac{1}{2} m g \qquad \Rightarrow \quad \textsl{T} = \frac{mgl}{2h}
[/tex]
I'd appreciate it if someone could help me out with the last part of (ii) and also checking whether I did the other parts correctly.
Thanks a lot :)
Honey [tex] \pi [/tex]