- #1
Dyon
- 30
- 2
Hi, I am trying to clear the mess of the terms used in fluid mechanics and get a clearer relationship between them. So I have summarized in the table below the relationship between viscosity and irrotationality of fluid flows.
Can somebody tell me if I got this right? Thanks.
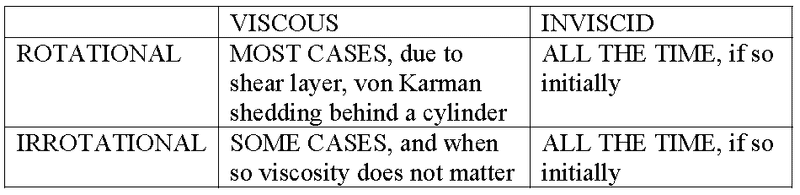
Can somebody tell me if I got this right? Thanks.