- #1
pat666
- 709
- 0
Homework Statement
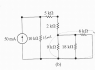
see attached for circuit
from your result from part b, use voltage division to find the voltage drop across the 2k ohm resistor. my result from b was 250V
part b question was voltage drop across 10K resistor
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
R_T=5k ohms
v=V_2k/V_T = 100v but the answer is 50V?
Thanks
Attachments
Last edited: