- #1
shanepitts
- 84
- 1
Pictured below was a problem shown in class with solution. I didn't have time to ask the professor a question about the last step involving an additive constant.
V is potential energy, re=Earth radius and z is distance from Earth's surface.
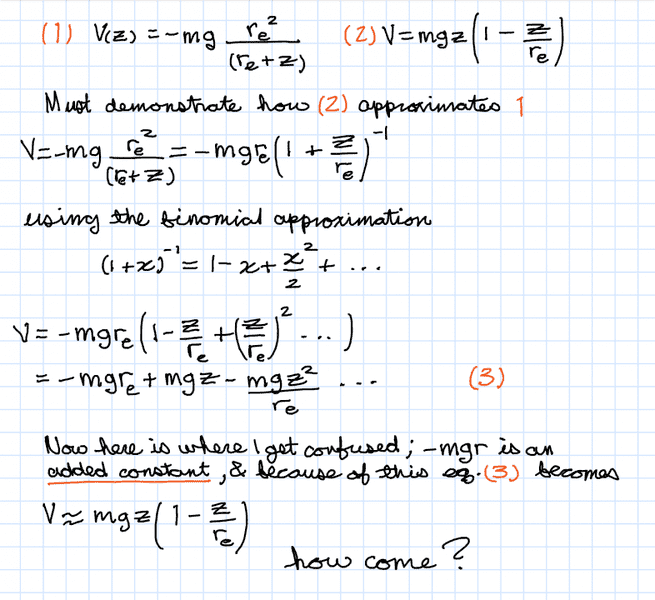
What is an additive constant, and how does it allow the last transformation?
V is potential energy, re=Earth radius and z is distance from Earth's surface.
What is an additive constant, and how does it allow the last transformation?