- #1
new6ton
- 223
- 5
My wine raman spectrometer has this laser module included in the box as extra (in case the original one get busted). I'd like to know what kind of laser is it.
 This is its front, note the bronze is the actual laser unit that is fixed with 3 screws in the silver casing:
This is its front, note the bronze is the actual laser unit that is fixed with 3 screws in the silver casing:
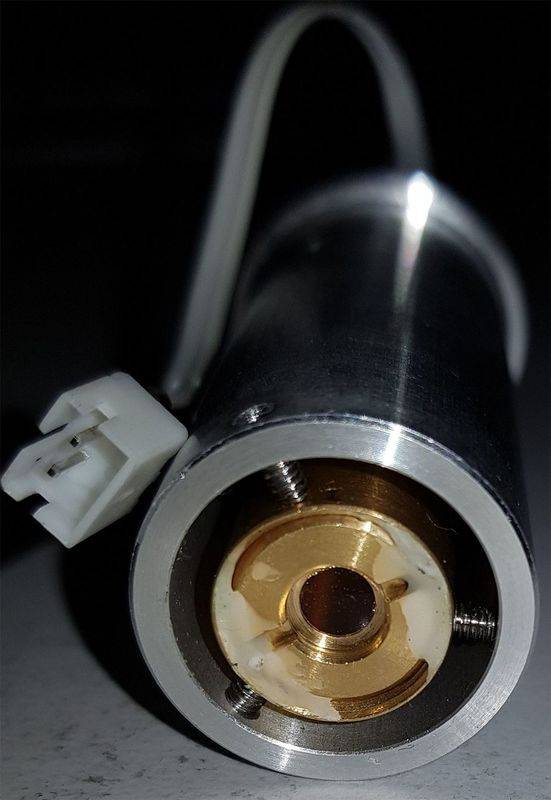

This is back of it:
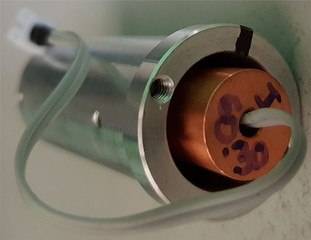
60.30 means that the mean output is 30 mW at 60% current at ambient conditions.
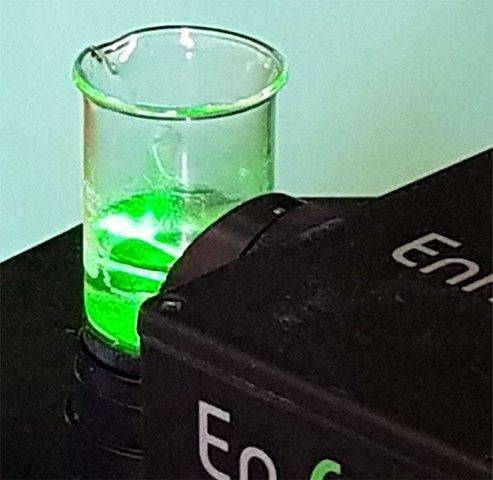
This is when my beaker with wine was scanned for sugar and other substances:
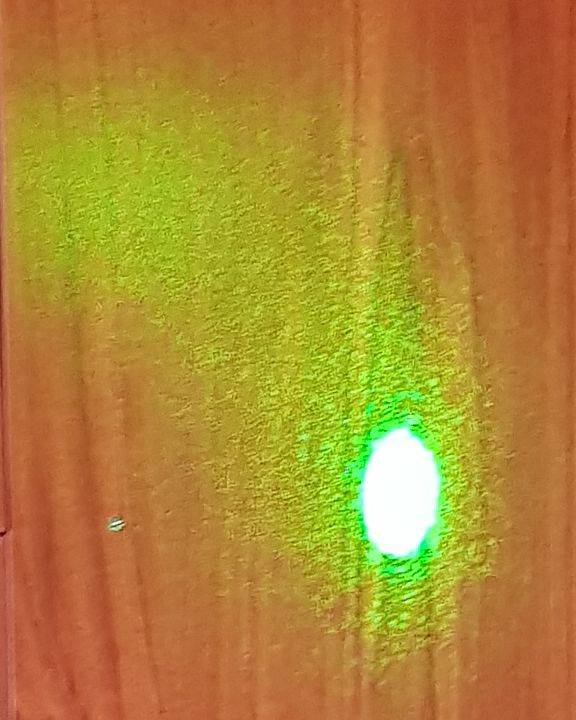
 This is the reflections of the laser at a laminated cabinet 1.1 meters away:
This is the reflections of the laser at a laminated cabinet 1.1 meters away:
 The safety goggles but without any rating:
The safety goggles but without any rating:

This is in the manual:
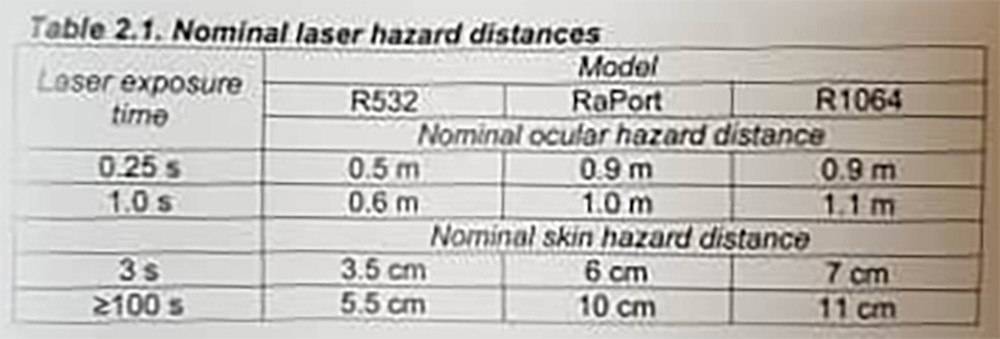 My model is R532 (Enspectr). Does it mean if the laser exposure time is 5 seconds, the NOHD (Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance) is higher than 0.6m?
My model is R532 (Enspectr). Does it mean if the laser exposure time is 5 seconds, the NOHD (Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance) is higher than 0.6m?
Someone in the internet told me about the laser (I don't have further comments that's why asking here)
"532nm says DPSS (Diode pumped solid state) with intracavity doubler.
It is really two lasers, an 808nm diode laser that provides optical pump power to drive a Nd-YAG laser crystal that operates at 1064nm. Within the YAG laser cavity is a non linear element that generates the output light by frequency doubling the 1064nm radiation to get to 532nm. I would expect the pump laser to be a few hundred mW or so to get 30mW of green.
Be careful, 30mW does not sound like much, but given the application it might have quite good beam quality (And may even be passively Q switched) in which case that is quite sufficient to cost you (or someone nearby) an eye. DPSS lasers also sometimes leak significant amounts of infra red along an axis that is not necessarily aligned with the main beam."
I'm concerned about the pump laser to be a few hundred mW. Is this leaked outside usually? And does a "passively Q switched" is even more powerful? And how true is it that the DPSS lasers also sometimes leak significant amounts of infra red along an axis that is not necessarily aligned with the main beam? How do you measure it?
I'm always more than 1 meter away from the beaker scanned with the green 532nm laser. But I always worry about the words that there is sometimes leak of significant amounts of infra red and the pump laser to be a few hundred mW.
Elsewhere. Scientists use it less than a meter away without any goggles. In the following video, the person holds the gem in front of the unit without any goggles:
Can't it affect him with the pump laser to be a few hundred mW and the "DPSS lasers also sometimes leak significant amounts of infra red along an axis that is not necessarily aligned with the main beam"?
This is back of it:
60.30 means that the mean output is 30 mW at 60% current at ambient conditions.
This is when my beaker with wine was scanned for sugar and other substances:
This is in the manual:
Someone in the internet told me about the laser (I don't have further comments that's why asking here)
"532nm says DPSS (Diode pumped solid state) with intracavity doubler.
It is really two lasers, an 808nm diode laser that provides optical pump power to drive a Nd-YAG laser crystal that operates at 1064nm. Within the YAG laser cavity is a non linear element that generates the output light by frequency doubling the 1064nm radiation to get to 532nm. I would expect the pump laser to be a few hundred mW or so to get 30mW of green.
Be careful, 30mW does not sound like much, but given the application it might have quite good beam quality (And may even be passively Q switched) in which case that is quite sufficient to cost you (or someone nearby) an eye. DPSS lasers also sometimes leak significant amounts of infra red along an axis that is not necessarily aligned with the main beam."
I'm concerned about the pump laser to be a few hundred mW. Is this leaked outside usually? And does a "passively Q switched" is even more powerful? And how true is it that the DPSS lasers also sometimes leak significant amounts of infra red along an axis that is not necessarily aligned with the main beam? How do you measure it?
I'm always more than 1 meter away from the beaker scanned with the green 532nm laser. But I always worry about the words that there is sometimes leak of significant amounts of infra red and the pump laser to be a few hundred mW.
Elsewhere. Scientists use it less than a meter away without any goggles. In the following video, the person holds the gem in front of the unit without any goggles:
Can't it affect him with the pump laser to be a few hundred mW and the "DPSS lasers also sometimes leak significant amounts of infra red along an axis that is not necessarily aligned with the main beam"?