- #1
nishantve1
- 76
- 1
This is not a homework question I encountered this while revisiting the Electric Dipoles .
First of all if someone explains me why the dipole
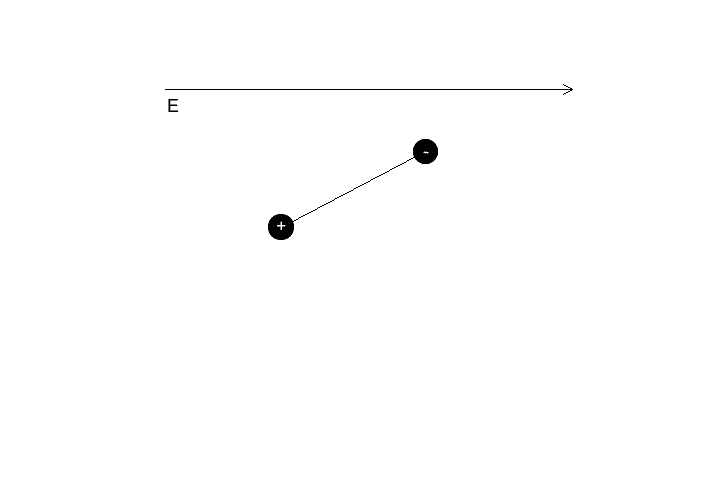
So in the image above which way should the dipole rotate ? Anti Clock Wise or Clock Wise .
What My intuition says is the Energy of a dipole is
U = -p.E
Which is -pEcosθ
So the Energy Graph would be
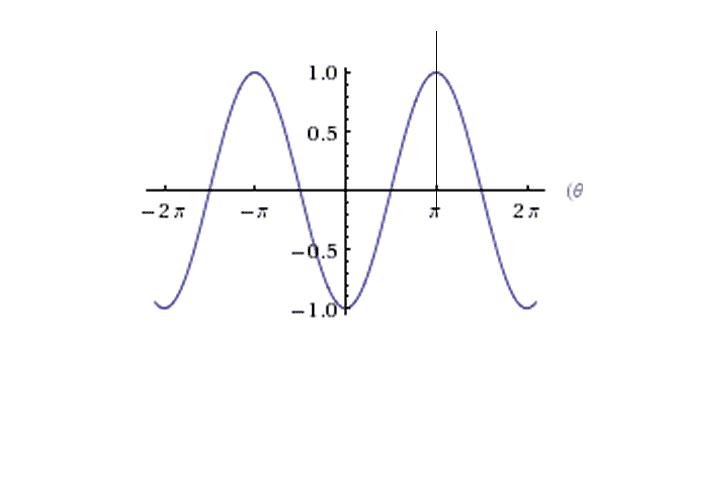
So there's a Stable Equilibrium at 0 and unstable equilibrium at ∏
So what I know is that angle is angle made between the E field and the Dipole moment .
What I am not getting is which way is the angle measured ? So if I rotate the dipole moment all the way to bottom will the angle still be same ? Like in the figure ?
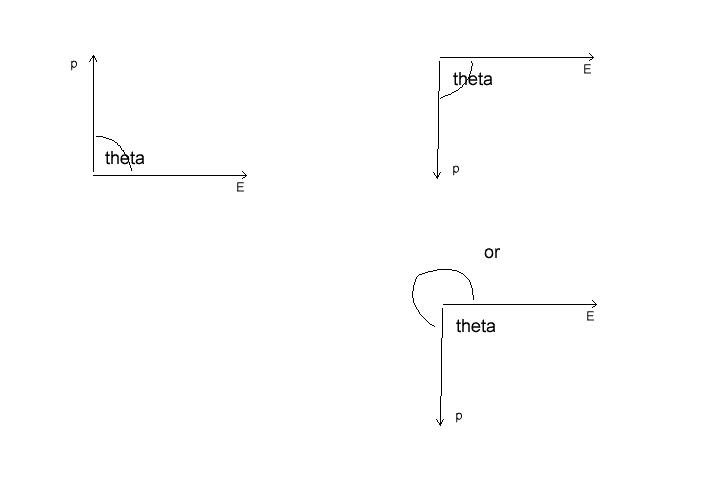
Also still which way the dipole rotate it seems easier for it rotate counter clockwise . But Will it ?
First of all if someone explains me why the dipole
So in the image above which way should the dipole rotate ? Anti Clock Wise or Clock Wise .
What My intuition says is the Energy of a dipole is
U = -p.E
Which is -pEcosθ
So the Energy Graph would be
So there's a Stable Equilibrium at 0 and unstable equilibrium at ∏
So what I know is that angle is angle made between the E field and the Dipole moment .
What I am not getting is which way is the angle measured ? So if I rotate the dipole moment all the way to bottom will the angle still be same ? Like in the figure ?
Also still which way the dipole rotate it seems easier for it rotate counter clockwise . But Will it ?