- #1
a5hl3yi
- 12
- 0
Question:
A beam is givn with an axial strain of 500x10^-6 and a Young's modulus of 200GNm^-2. work out the magnitude of the tenslie load.
Rlelvnt equations:
σ = YM x Axial strain
My workng:
So far I have worked out the stress of the beam to be:
36000000Nm^2
36MNm^2
But from here I don't know how to get the tensile load. Is there a formula I can use?
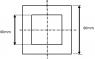
Picture of beam attached.
Thnx
A beam is givn with an axial strain of 500x10^-6 and a Young's modulus of 200GNm^-2. work out the magnitude of the tenslie load.
Rlelvnt equations:
σ = YM x Axial strain
My workng:
So far I have worked out the stress of the beam to be:
36000000Nm^2
36MNm^2
But from here I don't know how to get the tensile load. Is there a formula I can use?
Picture of beam attached.
Thnx