- #1
calculator20
- 47
- 0
Two isolated point charges -7μC and +2μC are at a fixed distance apart. At which point is is it possible for the electric field strength to be zero?
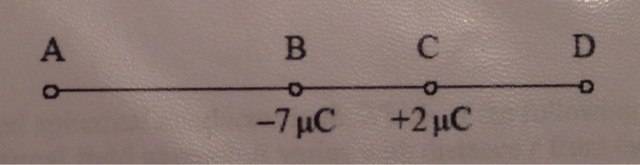
I don't know where to start with only 2 numbers and no distances. I know that E= kQ/r^2
I don't know where to start with only 2 numbers and no distances. I know that E= kQ/r^2