- #1
on1591
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
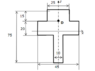
A vertical column has the horizontal cross sectional area shown in the attached image. The column carries a vertical compressive point load of 30kN applied at d. calculate the following:
a) The second central moments of area IZZ and Ixx
b) The maximum values of compressive and tensile stresses
c) The position on the cross section where the stress is zero
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I have done part a and got:
Ixx = 5.48E+5
IZZ = 1.75E+5
for part b i know the formulas for compressive stress and tensile stress. However they require a bending moment number. How do i calculate this?
Tensile = Mzc/Ixx
Compressive M(zmax-Zc)Ixx
Compressive stress due to point load F/A
C) I am not sure how to complete this part
Any help would be much appreciated