- 1,100
- 1,387
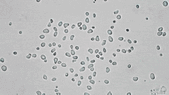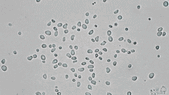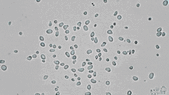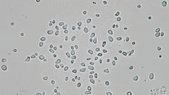
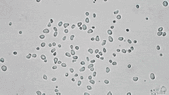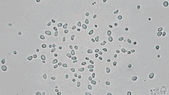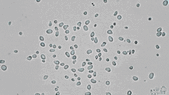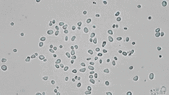
Stochastic calculus has come a long way since Robert Brown described the motion of pollen through a microscope in 1827. It’s now a key player in data science, quant finance, and mathematical biology. This article is drawn from notes I wrote for an undergraduate statistical physics course a few months ago. There won’t be any mathematical rigor.
Table of Contents
ToggleBrownian processes (and a Wetherspoons customer)Example: A drunken martingaleStochastic differential equations...
[url="https://www.physicsforums.com/insights/brownian-motions-and-quantifying-randomness-in-physical-systems/"]Continue reading...
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: