SUMMARY
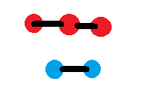
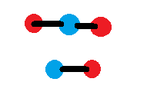
A bipartite graph can indeed be disconnected, allowing for two or more non-connected parts. According to the definition, a bipartite graph is represented as $G=(U,V,E)$, where $U$ and $V$ are the two distinct vertex sets and $E$ denotes the edges. If a bipartite graph is not connected, it can have multiple bipartitions, making the $(U,V,E)$ notation essential for clarity in applications. This confirms that disconnected components can still maintain the properties of bipartite graphs.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of graph theory concepts, specifically bipartite graphs
- Familiarity with graph notation, particularly $G=(U,V,E)$
- Basic knowledge of connected and disconnected graphs
- Ability to interpret mathematical definitions and properties of graphs
NEXT STEPS
- Research the properties of bipartite graphs in detail
- Explore examples of disconnected bipartite graphs
- Learn about applications of bipartite graphs in computer science
- Study the implications of multiple bipartitions in graph theory
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in mathematics, computer science, and data analysis who are interested in graph theory and its applications, particularly those focusing on bipartite graphs.