- #1
Guest432
- 48
- 2
I have read about gluons and pions, but I really don't understand what mediates the binding between the proton and neutron and how it happens!
Can you also explain this?
Can you also explain this?
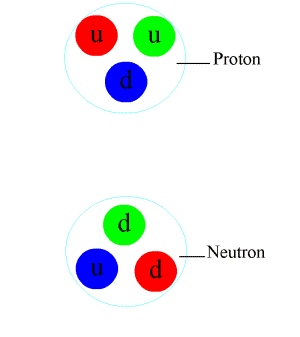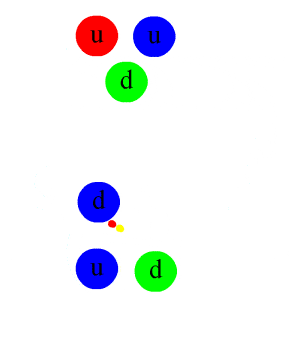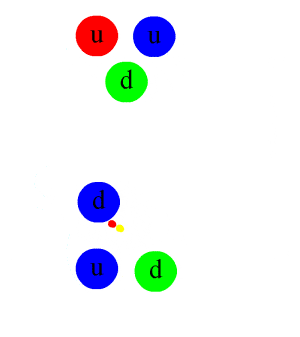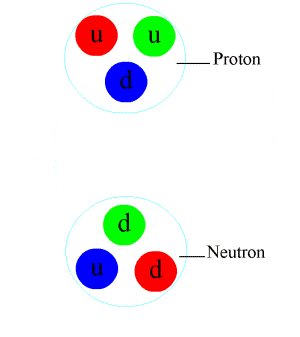
The nucleus is the central part of an atom, composed of protons and neutrons. It is important because it contains the majority of an atom's mass and houses the genetic information of an organism.
The nucleus is held together by the strong nuclear force, which is one of the four fundamental forces in nature. This force is responsible for binding protons and neutrons together despite their repulsive electric charges.
The strong nuclear force is mediated by particles called gluons, which carry the force between quarks (the building blocks of protons and neutrons). This force is much stronger than the electromagnetic force, allowing it to overcome the repulsive forces between protons and hold the nucleus together.
During nuclear reactions, the nucleus may gain or lose protons and neutrons, changing its composition. This can result in the formation of different elements or isotopes.
No, some nuclei are unstable and can undergo radioactive decay. This occurs when the strong nuclear force is not strong enough to hold the nucleus together, causing it to release particles and energy in order to become more stable.