wangvivi
- 10
- 0
- TL;DR
- how to measure the two-photon detuning in 3-level system
hi,everyone!
if i have a 3-level system,like this:
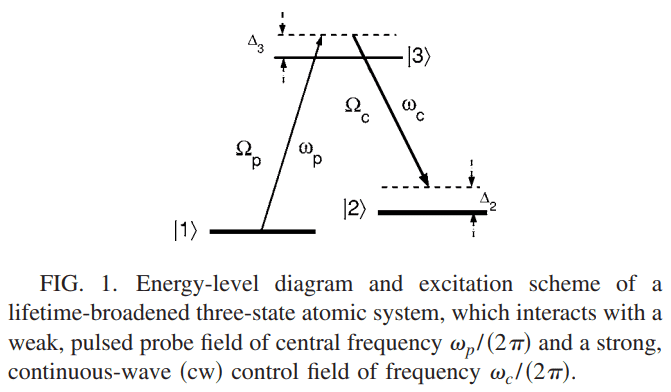
now,i want know how to measure the two-photon detuning in this system,and i‘ve known that,Δ2 and Δ3 are the two- and on-photon detunings,like this paper said:
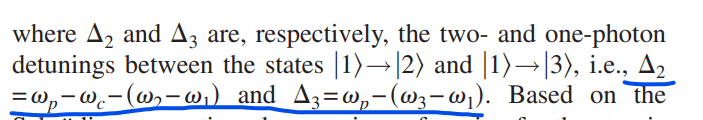
my questions are below:
1.how other researchers measure these two parameters?
they measure the beat frequency of probing light and controling light? or they use an interferometer to measure the frequency of probing light?
2.can anyone give me some examples for these parameter,like What is the approximate magnitude of two-photon detuning,if you have any paper or publication about that,please let me know,i would be so grateful to receive your guidance!
Have a nice day,everyone!
if i have a 3-level system,like this:
now,i want know how to measure the two-photon detuning in this system,and i‘ve known that,Δ2 and Δ3 are the two- and on-photon detunings,like this paper said:
my questions are below:
1.how other researchers measure these two parameters?
they measure the beat frequency of probing light and controling light? or they use an interferometer to measure the frequency of probing light?
2.can anyone give me some examples for these parameter,like What is the approximate magnitude of two-photon detuning,if you have any paper or publication about that,please let me know,i would be so grateful to receive your guidance!
Have a nice day,everyone!