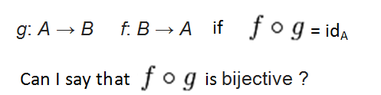Identity Function: Definition, Examples & Properties
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the identity function, specifically the definition and properties of the function denoted as $id_A: A \to A$. It is established that since the identity function is a bijection, the composition of the identity function with any other function $g$ results in another bijection, represented as $f \circ g: A \to A$ where $f \circ g: a \mapsto a$. This reinforces the fundamental property of identity functions in set theory and their role in function composition.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of bijections in set theory
- Familiarity with function composition
- Basic knowledge of mathematical notation
- Concept of identity functions
- Research the properties of bijective functions in set theory
- Learn about function composition and its implications
- Explore examples of identity functions in various mathematical contexts
- Study the role of identity functions in algebraic structures
Mathematicians, educators, and students studying set theory and function properties, particularly those interested in the implications of identity functions in mathematical analysis.
Similar threads
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 0 ·
- · Replies 17 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 54 ·
- · Replies 5 ·