- #1
Lo.Lee.Ta.
- 217
- 0
"The size cells can grow to is limited. Of the cells shown, which one"
Practice test question:
12) The size cells can grow to is limited. Of the
cells shown below, which one is likely to
experience the greatest difficulty as it grows
larger assuming it retains the same shape?
This is an awful picture! :( But it's how the image from the practice test is copied...
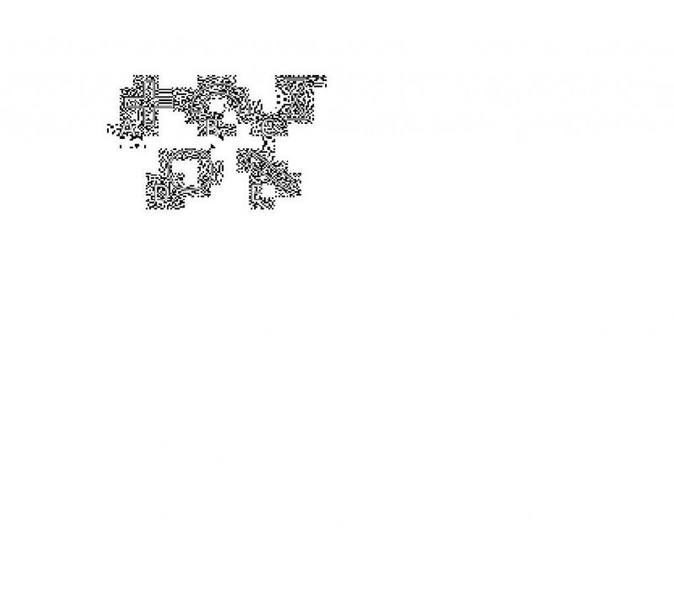
If you cannot tell what this is, A. plus sign, B. rainbow, C. hourglass, D. circle, E. thin rectangle.
Alright, my question first of all is- what are they meaning about grows larger? Do they mean surface area grows larger or volume grows larger?
Because I thought, if they meant surface area, the answer would would be E (thin rectangle), because neural cells somewhat have this long and thin shape as a way to increase surface area and signalling.
But then if they mean it grows larger in terms of volume, I think the answer would be D (circle), because I think a circle holds the most volume...?
I'm not sure about this... What would you say is the right answer here?
An answer key is not provided.
Thank you so much! :)
Practice test question:
12) The size cells can grow to is limited. Of the
cells shown below, which one is likely to
experience the greatest difficulty as it grows
larger assuming it retains the same shape?
This is an awful picture! :( But it's how the image from the practice test is copied...
If you cannot tell what this is, A. plus sign, B. rainbow, C. hourglass, D. circle, E. thin rectangle.
Alright, my question first of all is- what are they meaning about grows larger? Do they mean surface area grows larger or volume grows larger?
Because I thought, if they meant surface area, the answer would would be E (thin rectangle), because neural cells somewhat have this long and thin shape as a way to increase surface area and signalling.
But then if they mean it grows larger in terms of volume, I think the answer would be D (circle), because I think a circle holds the most volume...?
I'm not sure about this... What would you say is the right answer here?
An answer key is not provided.
Thank you so much! :)