- #1
Isabella F
- 3
- 0
Hi everyone. i have done a CFD smulation in fluent for a turbulent pipe flow and have plotted static pressure against distance x. from the graph i get a straight negtive gradient. i have been told that you should compare the pressure loss to Blasius equation and Darcy equation. How do i compare the pressure loss to this. thank you. the fluid is water, diameter is 50mm, inlet velocity is 1m/s and reynolds number 49760.
heres is the xy plot i get.
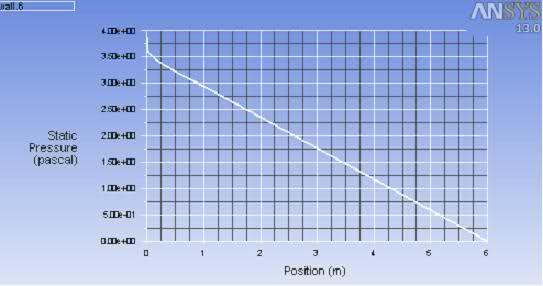
heres is the xy plot i get.