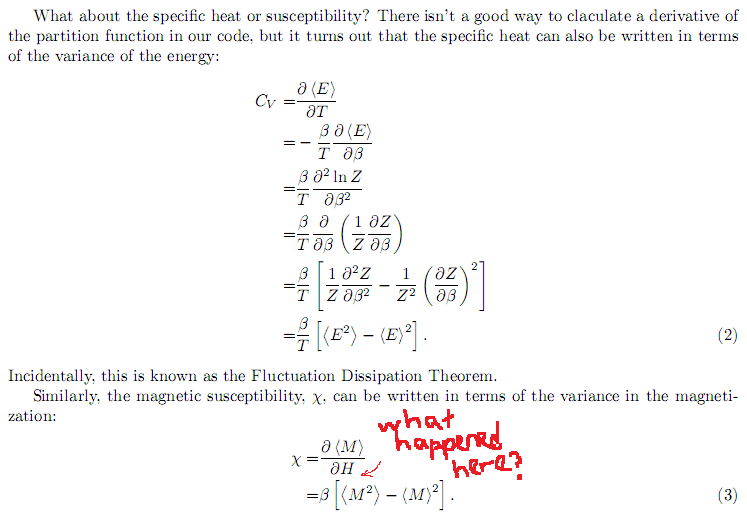SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on deriving the expression for magnetic susceptibility in the context of the simple 2D square Ising model. The key formula involves the partition function, expressed as Z = ∑{S_i} exp[K∑S_iS_j + βH∑i S_i]. The average magnetization M is defined as M = ∑i S_i, and the relationship between magnetic susceptibility and the variance of magnetization is established through derivatives of the partition function with respect to the external magnetic field H. Specifically, the first derivative yields the average magnetization, while the second derivative relates to the variance of magnetization.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Ising model and its partition function
- Familiarity with statistical mechanics concepts, particularly magnetic susceptibility
- Knowledge of derivatives in the context of thermodynamic quantities
- Basic grasp of the relationship between magnetization and external magnetic fields
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the partition function for the Ising model in greater detail
- Learn about the relationship between magnetic susceptibility and the variance of magnetization
- Explore the implications of the Ising model in higher dimensions, such as 3D
- Investigate the role of temperature (T) and Boltzmann constant (K) in magnetic systems
USEFUL FOR
This discussion is beneficial for physicists, particularly those specializing in statistical mechanics, as well as students and researchers interested in magnetic systems and the Ising model.