PHstud
- 12
- 0
Hello ! I am trying an exercice to get a better grip of what is the autocorellation meaning.
I know the mathematical formula, but let's consider a case.
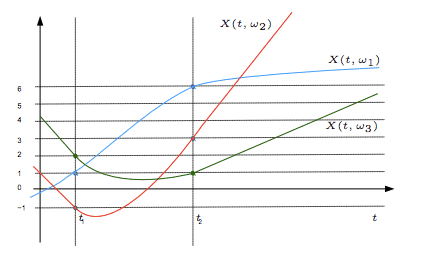
If in the case above, the probability of the red curve to happen (so w2) is Pr, the blue one Pb and the green on Pg, what would be the result of the autocorellation ?
Would it be something like the sum of the value X(t1,w1)*X(t2,w2)*Pb*Pr + X(t1,w1)*X(t3,w3)*Pb*Pg + ... ?
Thank you for helping me !
I know the mathematical formula, but let's consider a case.
If in the case above, the probability of the red curve to happen (so w2) is Pr, the blue one Pb and the green on Pg, what would be the result of the autocorellation ?
Would it be something like the sum of the value X(t1,w1)*X(t2,w2)*Pb*Pr + X(t1,w1)*X(t3,w3)*Pb*Pg + ... ?
Thank you for helping me !