namith11
- 26
- 0
Hey,
I want to know how to calculate the gear ratio of the given arrangement in the picture. I am not sure of how to calculate the gear ratio of two gears on the same shaft. Also the input gear is helical and the output gear is a spur gear. I have mentioned the number of gear teeth, i hope that is enough. I am very confused. Please help!
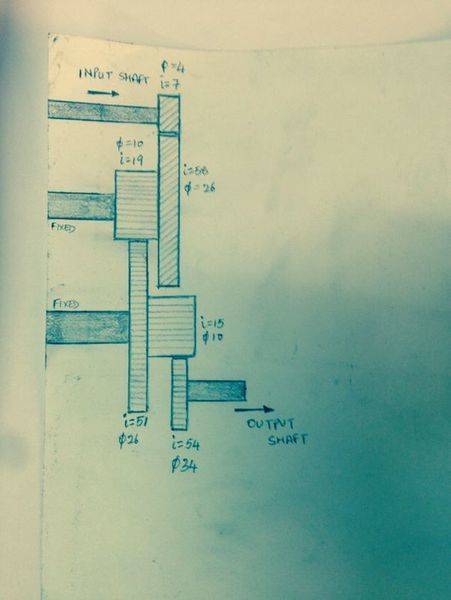
I want to know how to calculate the gear ratio of the given arrangement in the picture. I am not sure of how to calculate the gear ratio of two gears on the same shaft. Also the input gear is helical and the output gear is a spur gear. I have mentioned the number of gear teeth, i hope that is enough. I am very confused. Please help!