- #1
thecombover
- 2
- 0
A uniform spherical shell of mass 9.00 with diameter 54.0 has four small masses of mass 2.00 attached to its outer surface and equally spaced around it. This combination is spinning about an axis running through the center of the sphere and two of the small masses
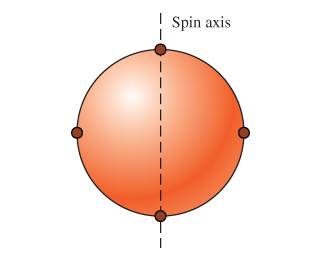
What friction torque is needed to reduce its angular speed from 80.0 to 55.0 in a time interval of 35.0 ?
What friction torque is needed to reduce its angular speed from 80.0 to 55.0 in a time interval of 35.0 ?