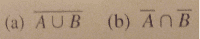SUMMARY
This discussion clarifies the notation used in set theory, particularly regarding complements and universal sets. The notation with a line over a set indicates negation, while the union (A U B) encompasses all elements in either set A or set B. The distinction between "not in (A or B)" and "(not in A) or (not in B)" is emphasized through examples, illustrating how the logical structure affects the truth values of statements. The intersection symbol (∩) is defined as the common elements between sets, while a bar over (A U B) signifies elements in the universal set that are not included in A or B.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic set theory concepts, including sets A and B.
- Familiarity with logical operators such as union (U), intersection (∩), and negation.
- Knowledge of universal sets and their role in set operations.
- Ability to interpret mathematical notation and symbols used in set theory.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of set theory, focusing on complements and universal sets.
- Learn about logical operators and their implications in mathematical statements.
- Explore the concept of Venn diagrams to visualize set operations and relationships.
- Investigate advanced topics in set theory, such as De Morgan's laws and their applications.
USEFUL FOR
Students of mathematics, educators teaching set theory, and anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of logical notation and set operations.