AEW
- 9
- 2
- TL;DR
- Construct some probability density functions for the maximum likelihood density estimation problem.
I have the following constrained optimization problem corresponding to the maximum likelihood density estimation:
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\text{maximize} && L(f) \\
&\text{subject to} && f \in H \\
&&& \int_a^b f(x) \mathop{}\!\mathrm{d} x = 1 \\
&&& f(x) \geq 0 \text{ for all } x \in [a,b].
\end{aligned}
$$
where ##x## is a random variable with probability density function (PDF) ##f## on an interval ##[a,b] \subset \textrm{IR}##, and ##H## is a subspace of ##L^1 [a,b]## (i.e., Lebesgue integrable on ##[a,b]##).
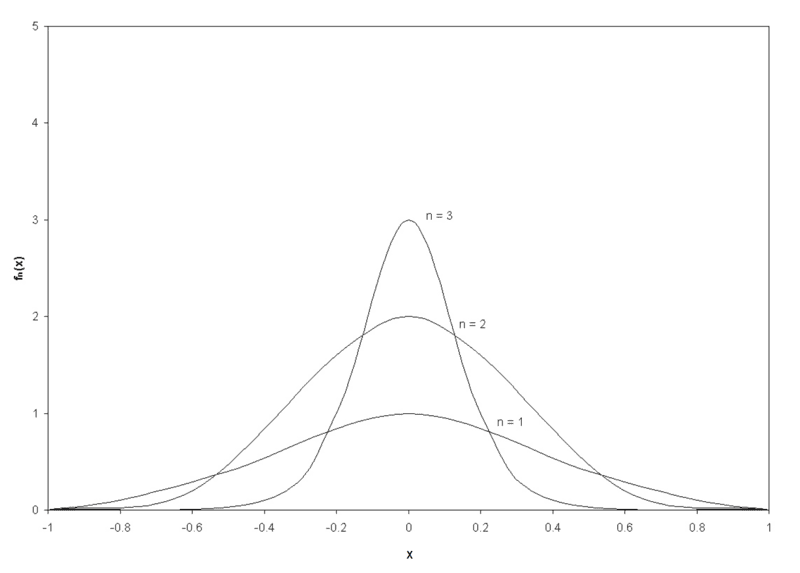
I need to construct some PDFs ##f_n## to prove the existence of a solution to the above optimization problem, which should have the following properties:
- Continuous and positive on the interval ##(-1,1)##,
- Integrates to one on the interval ##[-1,1]##,
- Vanishes at ##(-1)## and ##1##,
- Equal to ##n## at ##x=0## (e.g., ##f_2=2## at ##x=0##).
These functions ##f_n## are graphically represented in the figure below. My question is how to mathematically represent the functions ##f_n##.
Thanks.
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\text{maximize} && L(f) \\
&\text{subject to} && f \in H \\
&&& \int_a^b f(x) \mathop{}\!\mathrm{d} x = 1 \\
&&& f(x) \geq 0 \text{ for all } x \in [a,b].
\end{aligned}
$$
where ##x## is a random variable with probability density function (PDF) ##f## on an interval ##[a,b] \subset \textrm{IR}##, and ##H## is a subspace of ##L^1 [a,b]## (i.e., Lebesgue integrable on ##[a,b]##).
I need to construct some PDFs ##f_n## to prove the existence of a solution to the above optimization problem, which should have the following properties:
- Continuous and positive on the interval ##(-1,1)##,
- Integrates to one on the interval ##[-1,1]##,
- Vanishes at ##(-1)## and ##1##,
- Equal to ##n## at ##x=0## (e.g., ##f_2=2## at ##x=0##).
These functions ##f_n## are graphically represented in the figure below. My question is how to mathematically represent the functions ##f_n##.
Thanks.
Last edited: