sparkle123
- 172
- 0
Two loudspeakers are separated by 0.50 m on one wall of a room measuring 3.5 m by 7.0 m at a temperature of 22°C. Both speakers generate a constant amplitude sound of frequency 690 Hz, in phase with each other, radiating equally in all directions. What is the shortest distance x along the adjacent wall where an observer will hear no sound? Ignore any reflections from the walls.
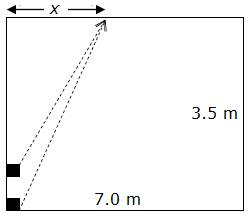
I think that constructive interference means the lengths differ by an odd multiple of half the wavelength (0.249 m).
so sqrt(x^2 + 3.5^2) - sqrt(x^2 + 3^2) = 0.249 (2k + 1)
But this is really complicated...Please give me a hint on how to start?
I think that constructive interference means the lengths differ by an odd multiple of half the wavelength (0.249 m).
so sqrt(x^2 + 3.5^2) - sqrt(x^2 + 3^2) = 0.249 (2k + 1)
But this is really complicated...Please give me a hint on how to start?