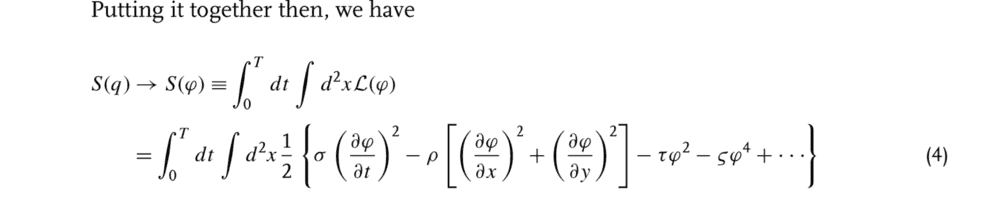SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the origin of the tau and sigma terms in the expression related to the self-interaction energy V of the field ##\varphi##, specifically in equation (2). These terms are identified as arbitrary coupling constants that arise when expressing the self-interaction part of the function V in a series of ##\varphi##. Additionally, a query regarding the transition from 3-momentum to 4-momentum in the Sidney Coleman lectures is raised, specifically concerning the dropping of the operator on the right side of the equation ##e^{i P . x}\alpha(p)e^{-i P . x} = e^{-i p . x}\alpha(p)##.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of quantum field theory concepts, particularly self-interaction energy.
- Familiarity with the notation and mathematical expressions used in quantum mechanics.
- Knowledge of the significance of coupling constants in field theories.
- Basic grasp of momentum representation in quantum mechanics.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of self-interaction energy in quantum field theory.
- Explore the role of coupling constants in various field theories.
- Learn about the transition from 3-momentum to 4-momentum in quantum mechanics.
- Review Sidney Coleman’s lectures for deeper insights into quantum field theory concepts.
USEFUL FOR
Students and researchers in quantum field theory, physicists interested in self-interaction energies, and anyone looking to deepen their understanding of momentum transitions in quantum mechanics.